Hazardous Area Classification: Innovative HVAC for Petrochemical
Hazardous area classification in petrochemical plants come with unique challenges for HVAC systems. These environments are full of explosive gases, flammable vapors, and volatile chemicals. Specialized HVAC solutions are essential…
Net Zero Energy Building: How to Achieve High-Performance
As the world faces the pressing challenges of climate change and energy consumption, Net Zero Energy Building (NZEB) have emerged as a crucial solution in the quest for sustainability. These…
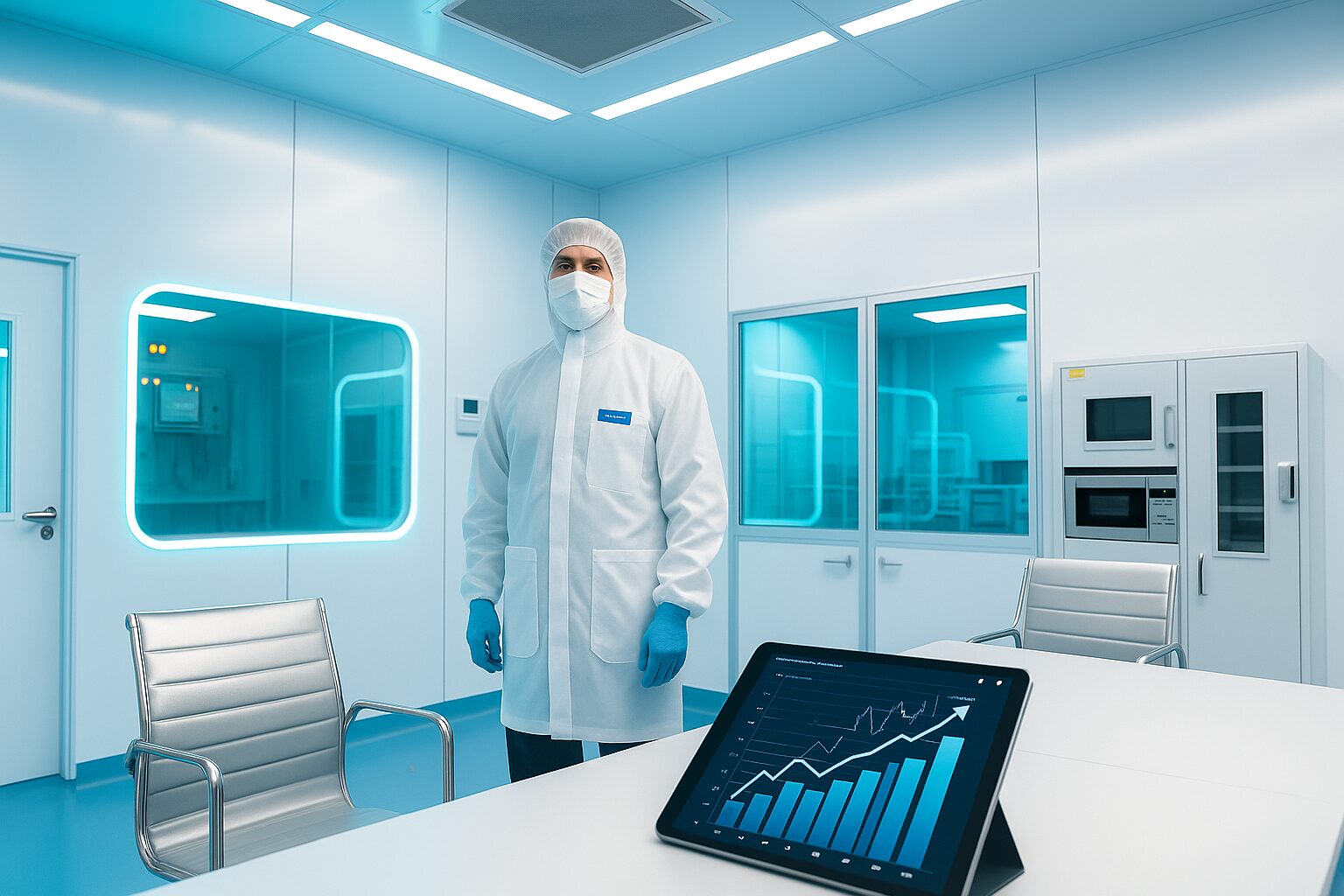
Disinfectant: How to Detect Hidden Problems in Sterile Cleanroom
Sterile cleanroom disinfectant are crucial in maintaining contamination-free environments. However, hidden problems in these disinfectants can undermine their effectiveness. This article will guide you through the process of detecting and…
Propane: What You Need to Know The Benefits in HVAC
As environmental concerns continue to drive innovations in building technologies, the adoption of propane based HVAC systems and natural ventilation strategies stands out for their significant benefits in energy efficiency…
Data Center: Maximize Financial Growth with Automated Payments
The Data Center construction industry faces a significant challenge with slow payment processes, causing financial strain and operational inefficiencies. The complex payment chain and lack of financial expertise among small-…
Cleanroom Technology: How Are Automation and Sustainability Reshaping?
In the realm of cleanroom technology, advancements in automation and sustainability are driving transformative changes. From pharmaceuticals to electronics manufacturing, industries reliant on sterile environments are increasingly integrating automated systems…
HVAC Systems: What are Hidden Impacts of Overdesigning
Overdesigning HVAC systems is a common yet overlooked practice that can have significant environmental and economic consequences. While a small safety margin is necessary for reliability, excessive overdesign can lead…
Chiller Plant: Do AI Optimize Energy Efficiency in Data Center?
In the digital age, data centers serve as vital hubs for storing, processing, and distributing vast amounts of information. Efficient operation of these centers relies heavily on robust HVAC systems,…
HVAC System: Why Sustainability is Important for Green Building
Sustainable HVAC system is revolutionizing green building design by providing energy-efficient, eco-friendly solutions that enhance indoor air quality and reduce environmental impact. These systems integrate advanced technologies and renewable energy…
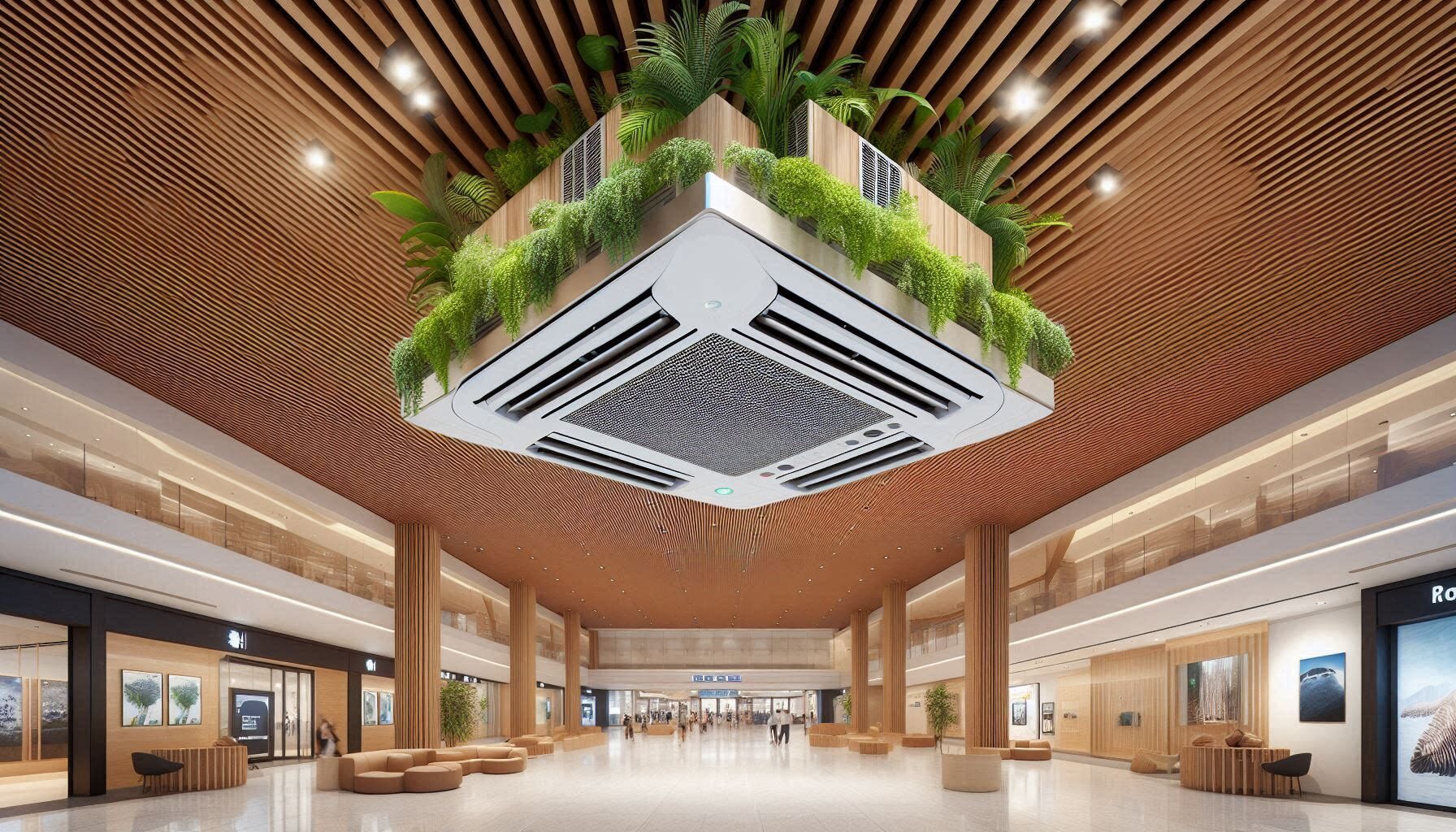
Cassette AC Unit: What are Latest Enhanced Innovations?
In today’s HVAC market, Cassette AC Unit air conditioning units have gained significant popularity due to their efficient cooling capabilities and discreet ceiling-mounted design. This comprehensive guide explores everything you…