Cleanroom Design: Challenges and How to Overcome
Cleanroom design is a cornerstone for industries that demand precision, sterility, and contamination control. From pharmaceuticals to biotechnology, cleanrooms are meticulously engineered environments where even the smallest oversight can compromise…
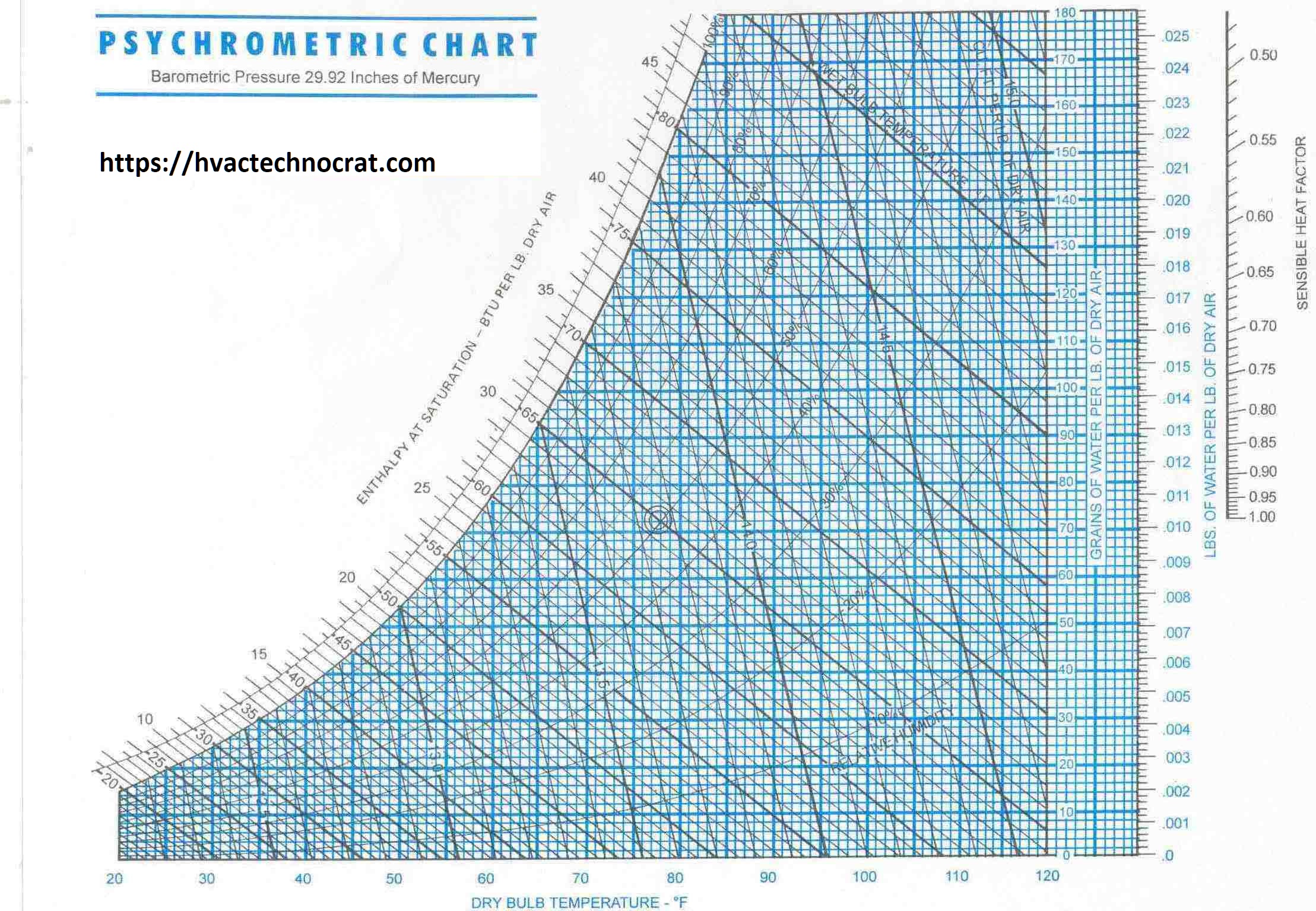
Psychrometry: Unlocking the Secrets for HVAC Systems
In the world of HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, Psychrometry plays a crucial role. It involves the study of air properties and their interactions with moisture, which is…
Desiccant Wheels in HVAC: How They Improve Indoor Air Quality
The desiccant wheel is an important part of HVAC systems, especially where dehumidification is critical. It is a rotating wheel with materials that absorb moisture from the air. This cycle…