Enhancing HVAC Systems Through Intelligent Automation and Emerging Technologies
Enhancing HVAC Systems Through Intelligent Automation and Emerging Technologies In today’s rapidly changing world, where climatic conditions are becoming more unpredictable and energy efficiency is paramount, the realm of Heating,…
Heat Recovery Wheels | A Comprehensive Guide on Design, Applications, and Best Practices
Heat Recovery Wheels | A Comprehensive Guide on Design, Applications, and Best Practices Description: Discover the significance of heat recovery wheels in HVAC systems and their role in energy-efficient solutions.…
HVAC Jobs | Exploring the Roles, Applications, and Skill Requirements
HVAC Jobs | Exploring the Roles, Applications, and Skill Requirements Welcome to the world of HVAC jobs, where heating, ventilation, and air conditioning converge to create comfortable indoor environments. In…
Airport HVAC: A Comprehensive Guide Design, Applications, and Best Practices
Airport HVAC: A Comprehensive Guide Design, Applications, and Best Practices Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Airport HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems. In this post, we’ll delve into…
Clean Room Design and Construction: Environmentally Controlled Area
Clean Room Design and Construction: Environmentally Controlled Area Introduction Clean room design is an essential discipline that ensures the creation of controlled environments to carryout the processes inside the cleanroom…
How AI is Revolutionizing HVAC Strategies for Data Centers: Navigating Challenges
How AI is Revolutionizing HVAC Strategies for Data Centers: Navigating Challenges Discover how the integration of Artificial Intelligence is reshaping HVAC strategies within data centers, overcoming challenges, and driving unprecedented…
How to Select the Right AC for Your Home
How to Select the Right AC for Your Home: A Comprehensive Guide Choosing the perfect air conditioner for your home is a pivotal decision that impacts your comfort, energy bills,…
Adapting Air Conditioning to a Warming World: Innovations for Sustainability
Adapting Air Conditioning to a Warming World: Innovations for Sustainability As global temperatures continue to rise due to climate change, the demand for cooling systems, particularly air conditioning, is surging.…
Clean Room: The Hidden Heroes of Everyday Life and Technology
What Defines a Clean Room? A clean room is a controlled environment where airborne particles, temperature, humidity, and pressure are carefully regulated to prevent contamination. These environments are indispensable in…
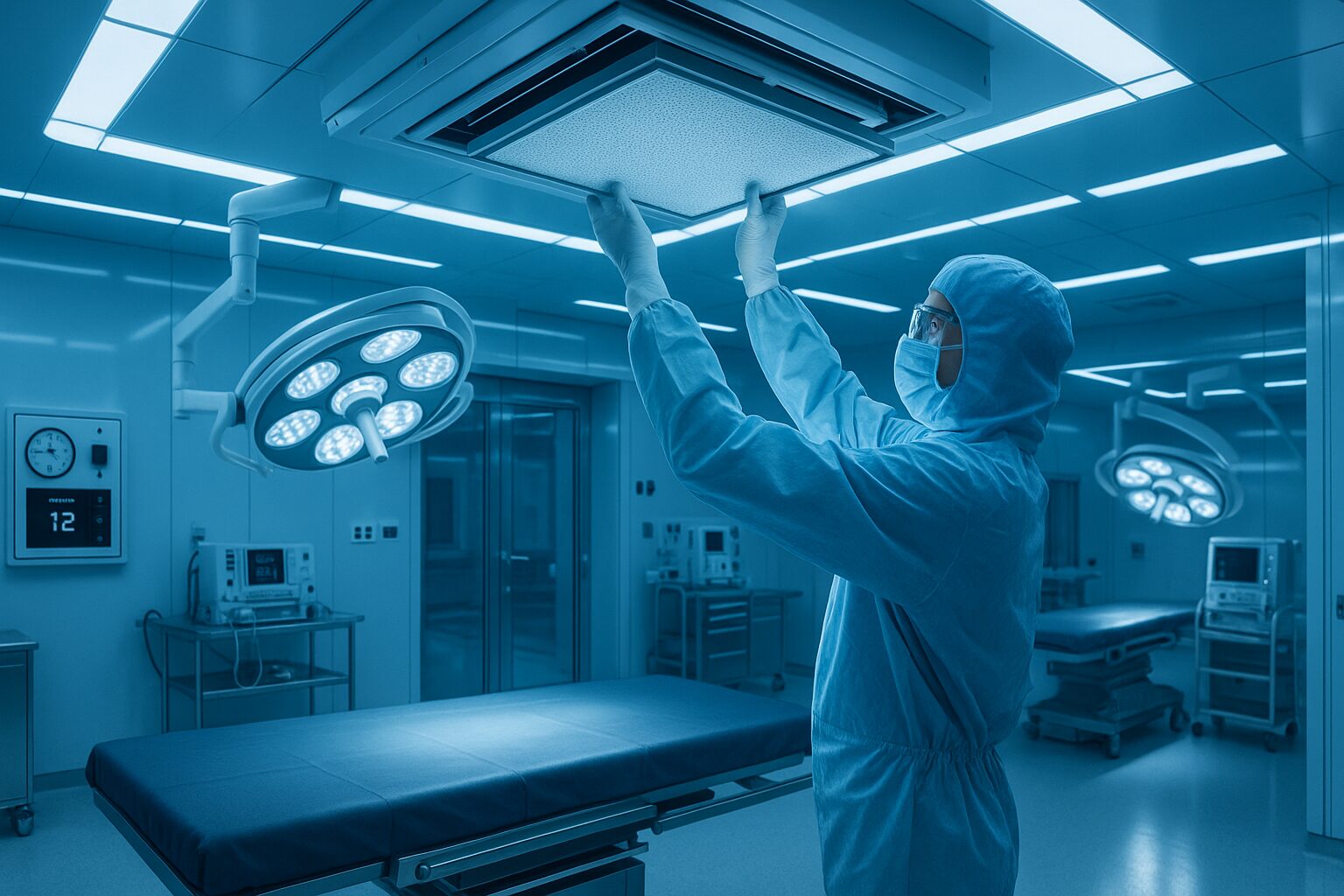
How to Replace and Maintain HEPA Filters in Operation Theatres
Why HEPA Filters Are Critical in Operation Theatres In operation theatres, HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters are the unsung heroes safeguarding patient outcomes. These filters capture 99.97% of airborne particles…