Air Handling Unit: Key and Best Practices of Technical Submittals
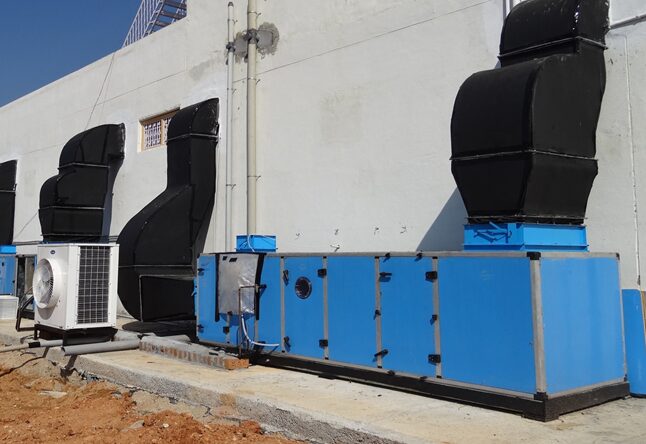
The packaged air handling unit (AHU) shall be factory assembled units in factory fabricated casings. Each unit shall be complete with aerofoil centrifugal blowers, motors, drives and guards, cooling coil…
Energy Savings with Multi Split AC: What You Need to Know
Efficient Multi Split AC Condensing Units provide advanced cooling solutions with multiple compressors and independent refrigerant circuits. Designed for various fan coil units, these units are factory-packaged for easy installation,…
Portable Air Conditioner: Do This Save Energy?
Portable Air Conditioner are split & ducted condensing units shall be with single compressors, each with its own independent refrigerant circuit couple with selected fan coil units (wall mounted, ceiling…
Cleanroom Temperature and Humidity: Why Its Critical to Control
Ensuring proper Cleanroom Temperature and Humidity Control is critical to maintaining the integrity of sensitive processes and products. Cleanrooms used in various industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology and electronics require…
Why Indoor Air Quality Matters in Commercial Spaces
Understanding the importance of indoor air quality (IAQ) in commercial spaces is critical to health, productivity, and overall well-being. Poor air quality can lead to various health problems and affect…
How to Design Effective 100% Exhaust Air System
Effective ventilation is crucial in various industries. Designing a 100% exhaust air system effectively removes contaminated air from the facility. This guide covers key features, considerations, and best practices for…
How to Optimize HVAC Systems for Cleanroom Pressure Control?
Maintaining the integrity of cleanrooms is crucial in industries like pharmaceuticals, electronics, and biotechnology. The role of cleanroom pressure differential in HVAC systems is a fundamental aspect of ensuring this…
What Makes Precision AC the Best Choice for Data Center?
Precision AC units are required to maintain optimal environmental conditions in critical settings such as data centers and laboratories. These units provide precise Temperature Control , Humidity Control , and…
Petrochemical: When to Perform Energy Audits for HVAC Systems
Understanding when to perform energy audits for Petrochemical HVAC systems is critical to optimizing energy efficiency, reducing operating costs, and ensuring environmental friendliness. This article examines the timing of these…
Cleanroom: What Are the Best Practices for Particle Control?
It is important to understand the importance of cell control in the cleanroom environment to maintain hygiene and ensure the quality of the product. This article analyzes how effective cell…