HVAC System: Why Sustainability is Important for Green Building
Sustainable HVAC system is revolutionizing green building design by providing energy-efficient, eco-friendly solutions that enhance indoor air quality and reduce environmental impact. These systems integrate advanced technologies and renewable energy…
Cassette AC Unit: What are Latest Enhanced Innovations?
In today’s HVAC market, Cassette AC Unit air conditioning units have gained significant popularity due to their efficient cooling capabilities and discreet ceiling-mounted design. This comprehensive guide explores everything you…
Basement Ventilation System: What Are the Best Practices?
Understanding Basement Ventilation Systems: A Comprehensive Guide Basement ventilation systems play a crucial role in maintaining indoor air quality and ensuring a healthy environment in residential and commercial buildings. Whether…
Air Cooler: How To Upgrade and Enhance Energy Efficiency?
Air cooler, also known as evaporative coolers, are increasingly popular alternatives to traditional air conditioning systems due to their energy efficiency and environmental benefits. They work by using the natural…
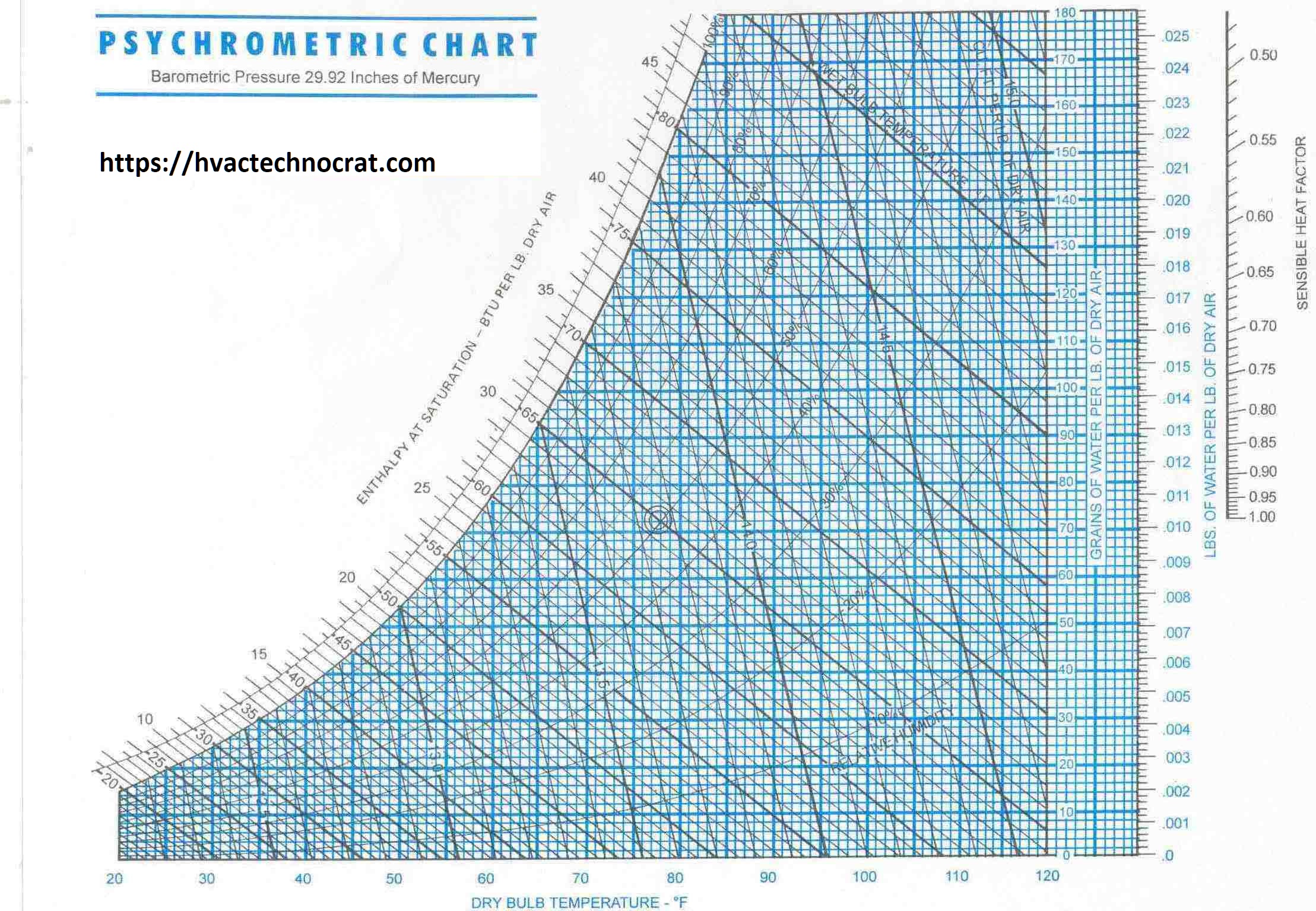
Psychrometry: Unlocking the Secrets for HVAC Systems
In the world of HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, Psychrometry plays a crucial role. It involves the study of air properties and their interactions with moisture, which is…
Heat Load Calculation: Everything You Need to Know
Heat load calculation, a fundamental aspect of HVAC system design, involves calculating the heat energy required to maintain desired indoor temperatures. This process starts by understanding the space’s dimensions, occupancy…
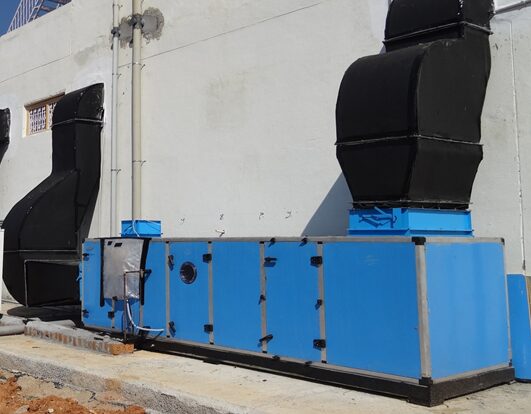
AHU: Exploring Specifications Which You Need to Know
An Air Handling Unit (AHU) is a critical component in HVAC systems, designed to regulate and circulate air. It houses essential elements like fans, filters, heating and cooling coils, and…
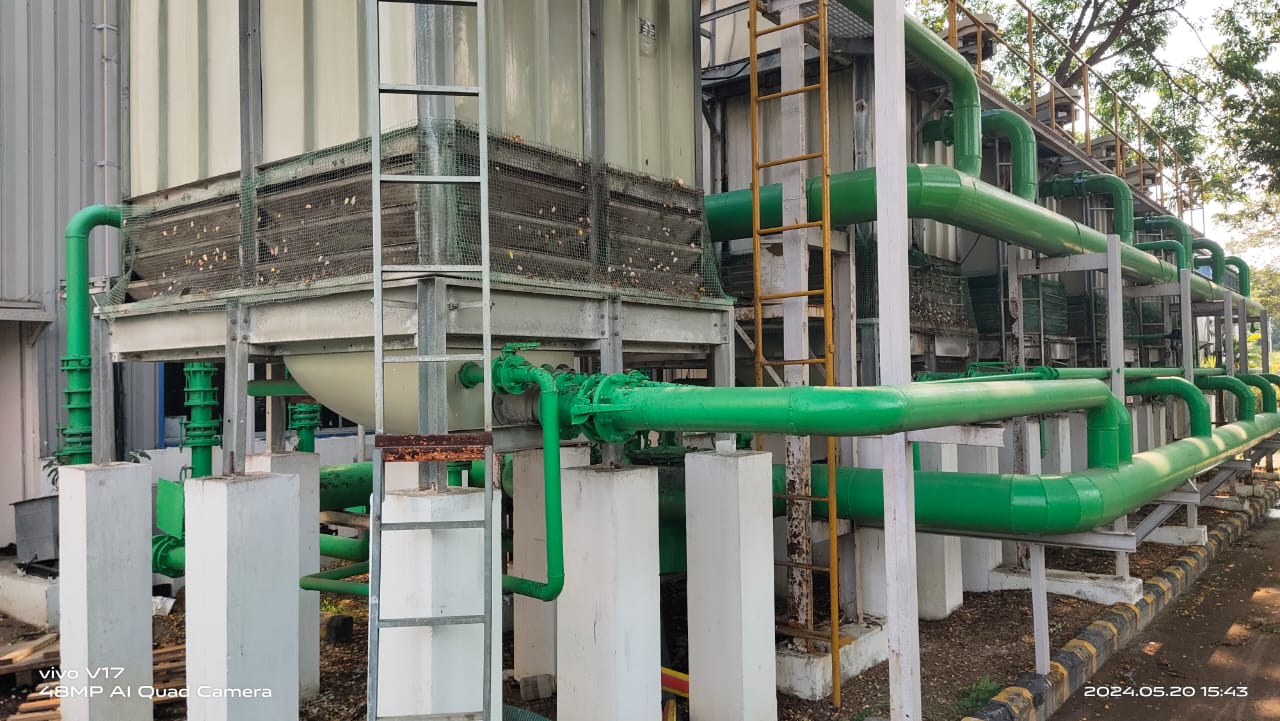
Cooling Tower: How to Enhance Energy Efficiency in Buildings
What is Cooling Tower in HVAC Systems A cooling tower is a specialized heat rejection device that extracts waste heat to the atmosphere through the cooling of a water stream…
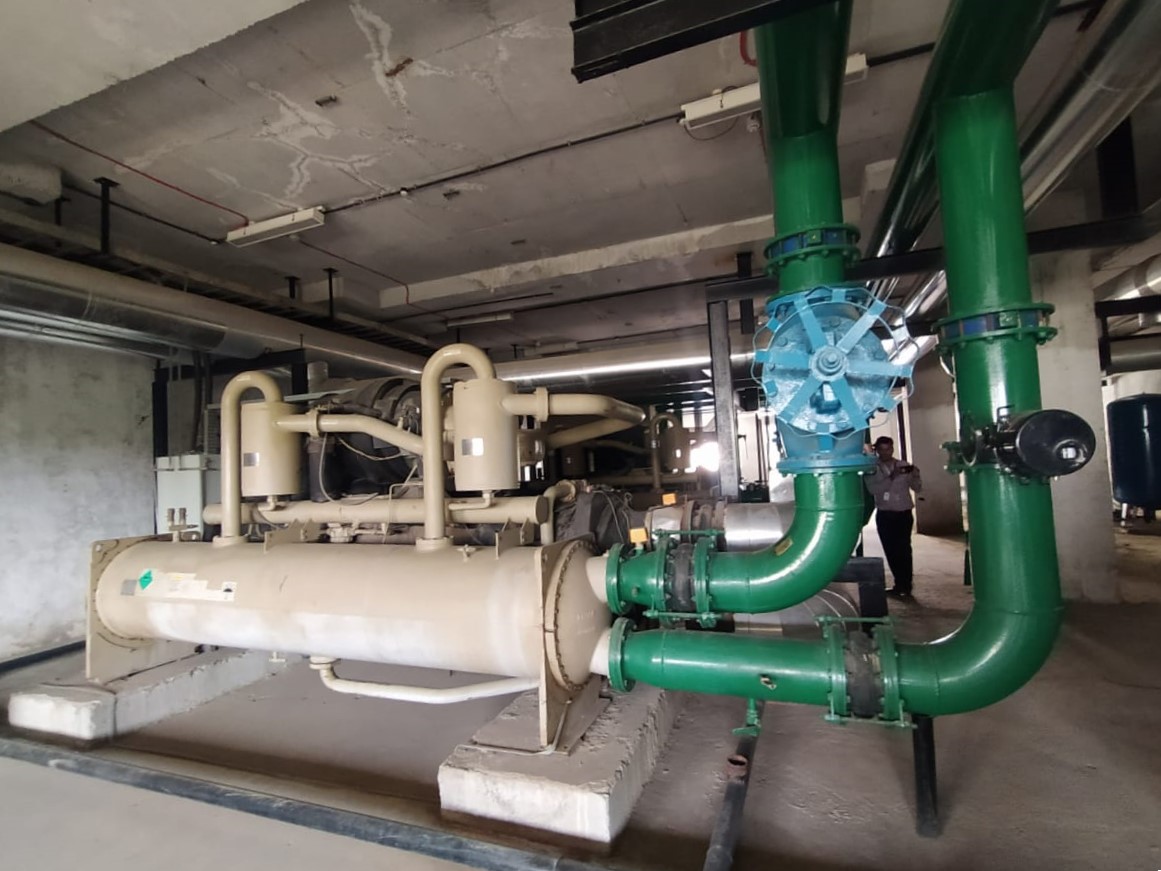
HVAC Chiller: The Ultimate Guide on Applications, and Benefits
An HVAC chiller is a vital component in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems designed to provide cooling by removing heat from a fluid via a refrigeration cycle. It…
VAV: How to Select the Best Units for BMS Integration
VAV also called as Variable Air Volume boxes are integral to modern HVAC systems, providing efficient and flexible temperature control. Integrating these units with Building Management Systems (BMS) enhances the…