HVAC Consultant: How they Can Save You Money and Energy
In today’s competitive industrial and commercial landscape, optimizing HVAC systems isn’t just about comfort—it’s about cost savings, energy efficiency, and sustainability. Whether you manage a pharmaceutical cleanroom, a semiconductor facility, a data…
Chiller Plant: Do AI Optimize Energy Efficiency in Data Center?
In the digital age, data centers serve as vital hubs for storing, processing, and distributing vast amounts of information. Efficient operation of these centers relies heavily on robust HVAC systems,…
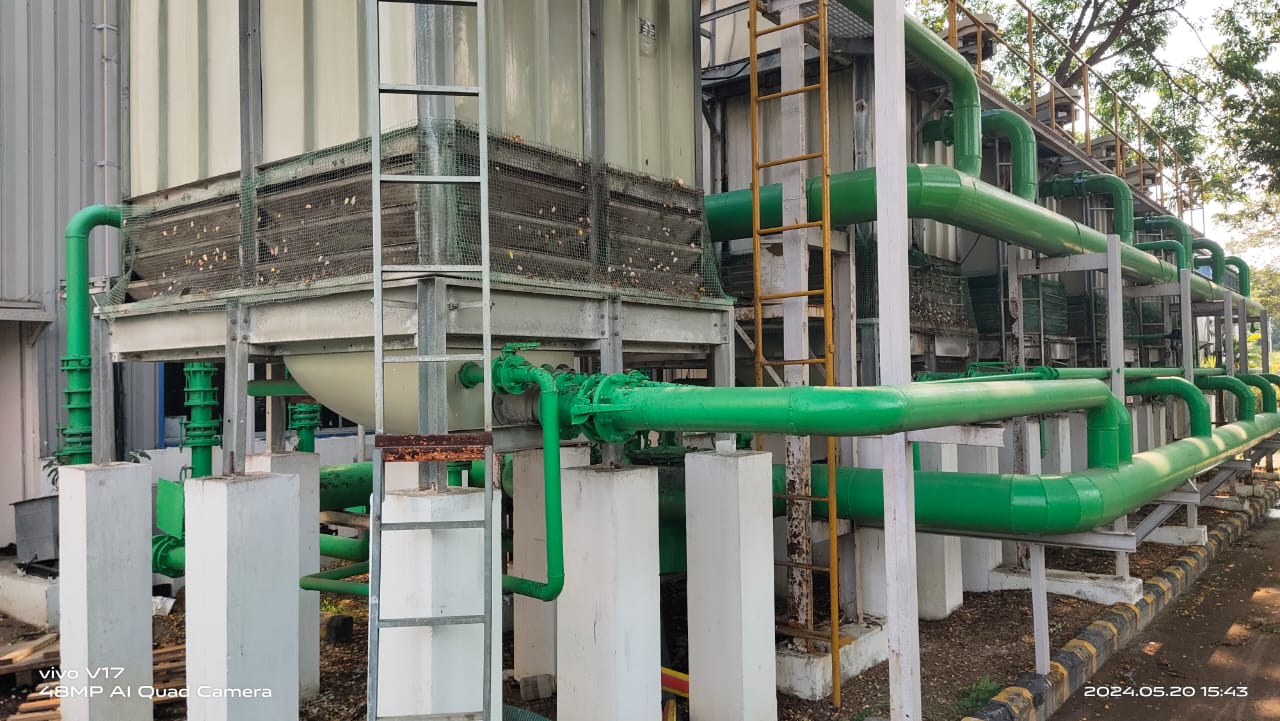
Cooling Tower: How to Enhance Energy Efficiency in Buildings
What is Cooling Tower in HVAC Systems A cooling tower is a specialized heat rejection device that extracts waste heat to the atmosphere through the cooling of a water stream…
How to Choose the Right Geothermal HVAC System
Geothermal HVAC systems significantly reduce energy bills by harnessing the stable temperatures found underground. Unlike traditional systems that rely on fluctuating outdoor air temperatures, geothermal systems use the constant temperature…
How BTU Meters Enhance Energy Efficiency in HVAC Systems
Introduction: BTU meters play a vital role in HVAC systems by measuring the heat energy exchanged in a controlled environment. Understanding their functionality, applications and installation requirements is essential to…
Energy Savings with Multi Split AC: What You Need to Know
Efficient Multi Split AC Condensing Units provide advanced cooling solutions with multiple compressors and independent refrigerant circuits. Designed for various fan coil units, these units are factory-packaged for easy installation,…