HVAC Consultant: How they Can Save You Money and Energy
In today’s competitive industrial and commercial landscape, optimizing HVAC systems isn’t just about comfort—it’s about cost savings, energy efficiency, and sustainability. Whether you manage a pharmaceutical cleanroom, a semiconductor facility, a data…
Balancing Valve: How to Select the Right One for HVAC System?
In HVAC systems, maintaining the correct balance of water or air flow is essential for optimal performance and energy efficiency. This is where balancing valve come into play. These crucial…
Control Valve: How to Choose the Right One for HVAC System?
Control valve play a pivotal role in managing HVAC systems, ensuring they operate efficiently and effectively. These valves regulate the flow of air or fluids, which helps maintain optimal temperature…
HVAC Valves: How To Select Different Types?
Choosing the right HVAC valves is vital for your heating and cooling system’s efficiency and longevity. With numerous valve types available, each with specific functions, it’s essential to understand their…
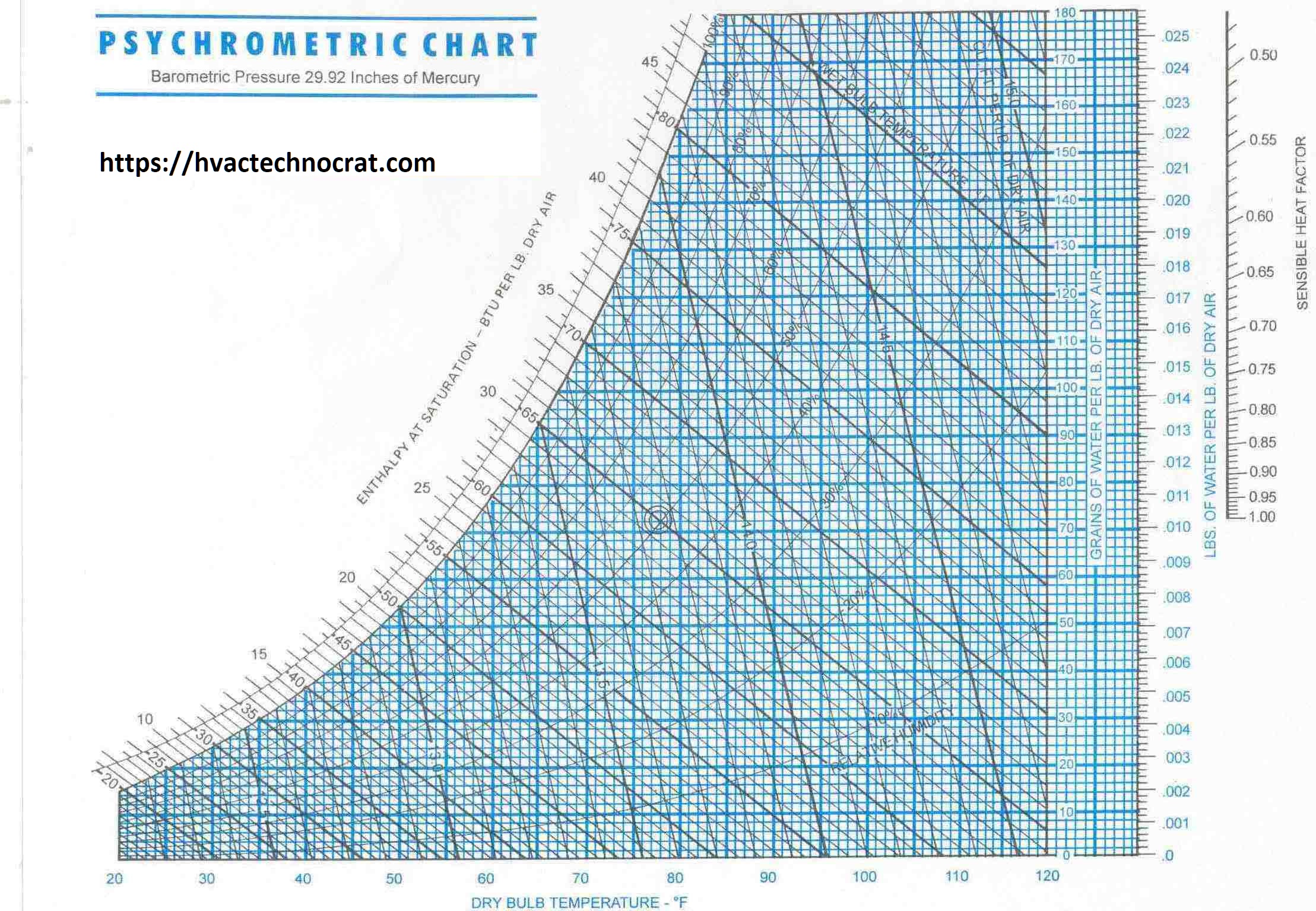
Psychrometry: Unlocking the Secrets for HVAC Systems
In the world of HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, Psychrometry plays a crucial role. It involves the study of air properties and their interactions with moisture, which is…
Cooling Tower: How to Enhance Energy Efficiency in Buildings
What is Cooling Tower in HVAC Systems A cooling tower is a specialized heat rejection device that extracts waste heat to the atmosphere through the cooling of a water stream…
How BTU Meters Enhance Energy Efficiency in HVAC Systems
Introduction: BTU meters play a vital role in HVAC systems by measuring the heat energy exchanged in a controlled environment. Understanding their functionality, applications and installation requirements is essential to…
Desiccant Wheels in HVAC: How They Improve Indoor Air Quality
The desiccant wheel is an important part of HVAC systems, especially where dehumidification is critical. It is a rotating wheel with materials that absorb moisture from the air. This cycle…
Chilled Water Pipe: How to Enhance HVAC Systems
In the modern world of construction and industrial processes, the proper functioning of heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) systems is critical to maintaining comfort, productivity and environmental sustainability. The…
Kitchen Exhaust System: How to Design an Efficient HVAC Solution
Kitchen exhaust system play a vital role in maintaining air quality, safety and comfort in commercial and residential spaces. In the HVAC realm, these systems are essential components that cater…