HVAC Consultant: How they Can Save You Money and Energy
In today’s competitive industrial and commercial landscape, optimizing HVAC systems isn’t just about comfort—it’s about cost savings, energy efficiency, and sustainability. Whether you manage a pharmaceutical cleanroom, a semiconductor facility, a data…
India Semiconductor: Innovative for Cleanroom Tech for Growth
India’s semiconductor industry is surging, driven by global demand for electronics and government initiatives like the Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme. At the heart of this growth lies cleanroom technology—a field…
Smart HVAC Systems: How to Protect in Data Centers
As data centers evolve into smarter, more interconnected ecosystems, the role of Smart HVAC systems has expanded beyond temperature control. Modern smart HVAC systems integrate with building automation networks, IoT…
HVAC Systems: What are Hidden Impacts of Overdesigning
Overdesigning HVAC systems is a common yet overlooked practice that can have significant environmental and economic consequences. While a small safety margin is necessary for reliability, excessive overdesign can lead…
Heat Load Calculation: Everything You Need to Know
Heat load calculation, a fundamental aspect of HVAC system design, involves calculating the heat energy required to maintain desired indoor temperatures. This process starts by understanding the space’s dimensions, occupancy…
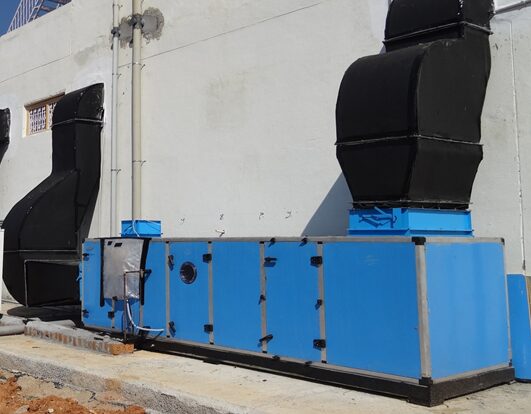
AHU: Exploring Specifications Which You Need to Know
An Air Handling Unit (AHU) is a critical component in HVAC systems, designed to regulate and circulate air. It houses essential elements like fans, filters, heating and cooling coils, and…
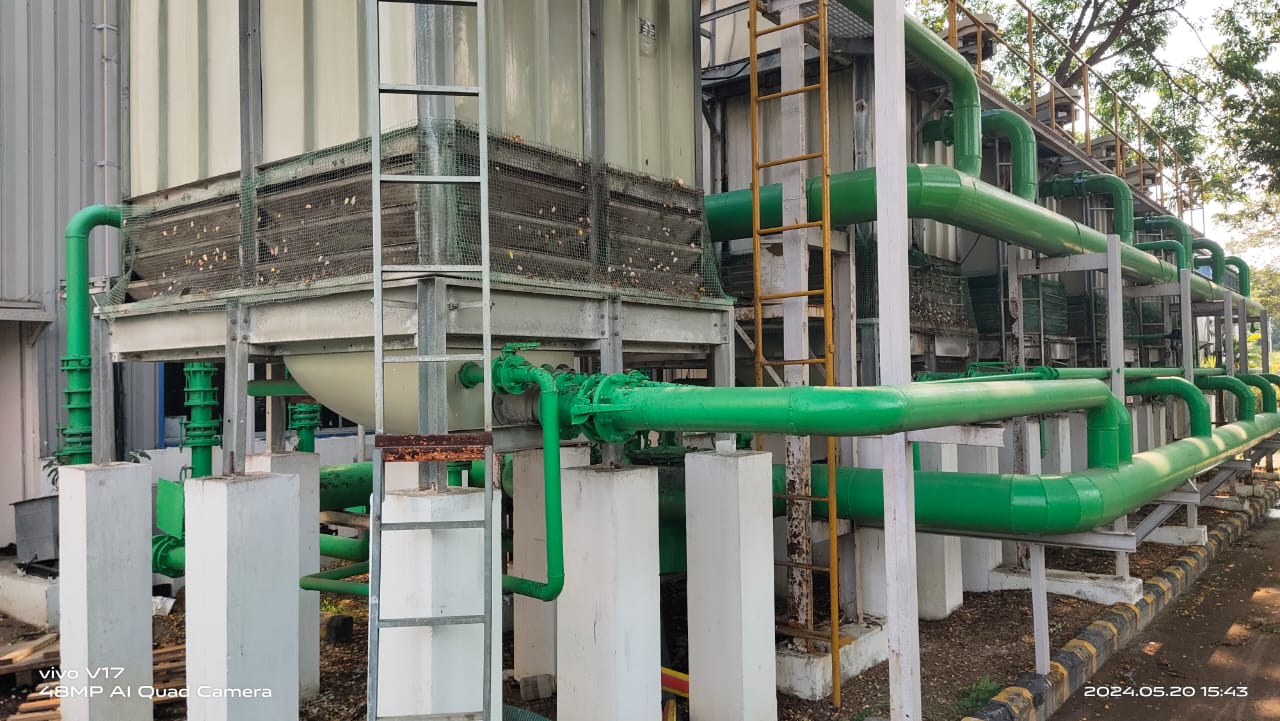
Cooling Tower: How to Enhance Energy Efficiency in Buildings
What is Cooling Tower in HVAC Systems A cooling tower is a specialized heat rejection device that extracts waste heat to the atmosphere through the cooling of a water stream…
VAV: How to Select the Best Units for BMS Integration
VAV also called as Variable Air Volume boxes are integral to modern HVAC systems, providing efficient and flexible temperature control. Integrating these units with Building Management Systems (BMS) enhances the…