3D Printed Ductwork is the Next Big Thing in HVAC
3D Printed Ductwork is the Next Big Thing in HVAC The HVAC industry is on the brink of a quiet revolution, and it’s being shaped layer by layer—literally. 3D printed…
Explosion Proof AHU: How to Choose the Best in Petrochemical
Choosing the best explosion proof AHU (Air Handling Unit) is crucial for ensuring safety in hazardous environments. These specialized units are designed to prevent sparks and contain potential explosions, protecting…
Hazardous Area Classification: Innovative HVAC for Petrochemical
Hazardous area classification in petrochemical plants come with unique challenges for HVAC systems. These environments are full of explosive gases, flammable vapors, and volatile chemicals. Specialized HVAC solutions are essential…
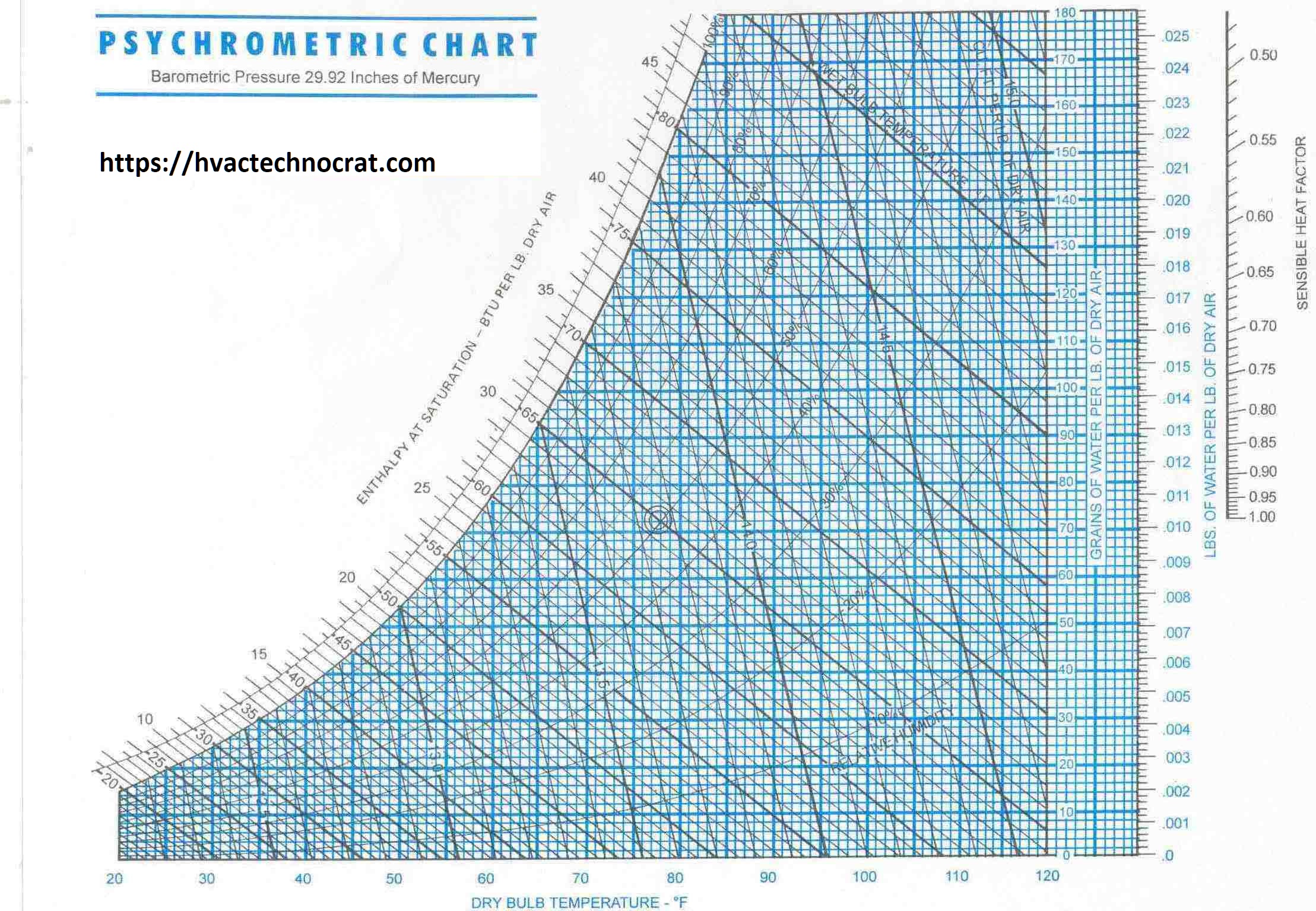
Psychrometry: Unlocking the Secrets for HVAC Systems
In the world of HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, Psychrometry plays a crucial role. It involves the study of air properties and their interactions with moisture, which is…
Heat Load Calculation: Everything You Need to Know
Heat load calculation, a fundamental aspect of HVAC system design, involves calculating the heat energy required to maintain desired indoor temperatures. This process starts by understanding the space’s dimensions, occupancy…
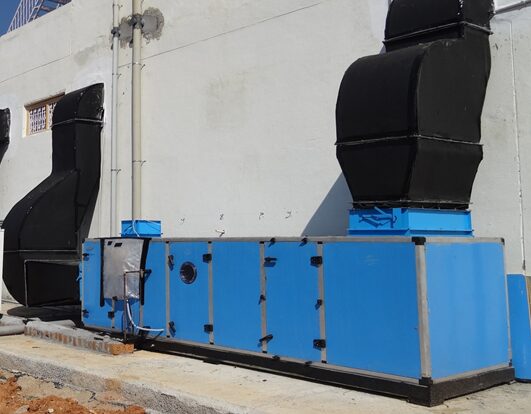
AHU: Exploring Specifications Which You Need to Know
An Air Handling Unit (AHU) is a critical component in HVAC systems, designed to regulate and circulate air. It houses essential elements like fans, filters, heating and cooling coils, and…
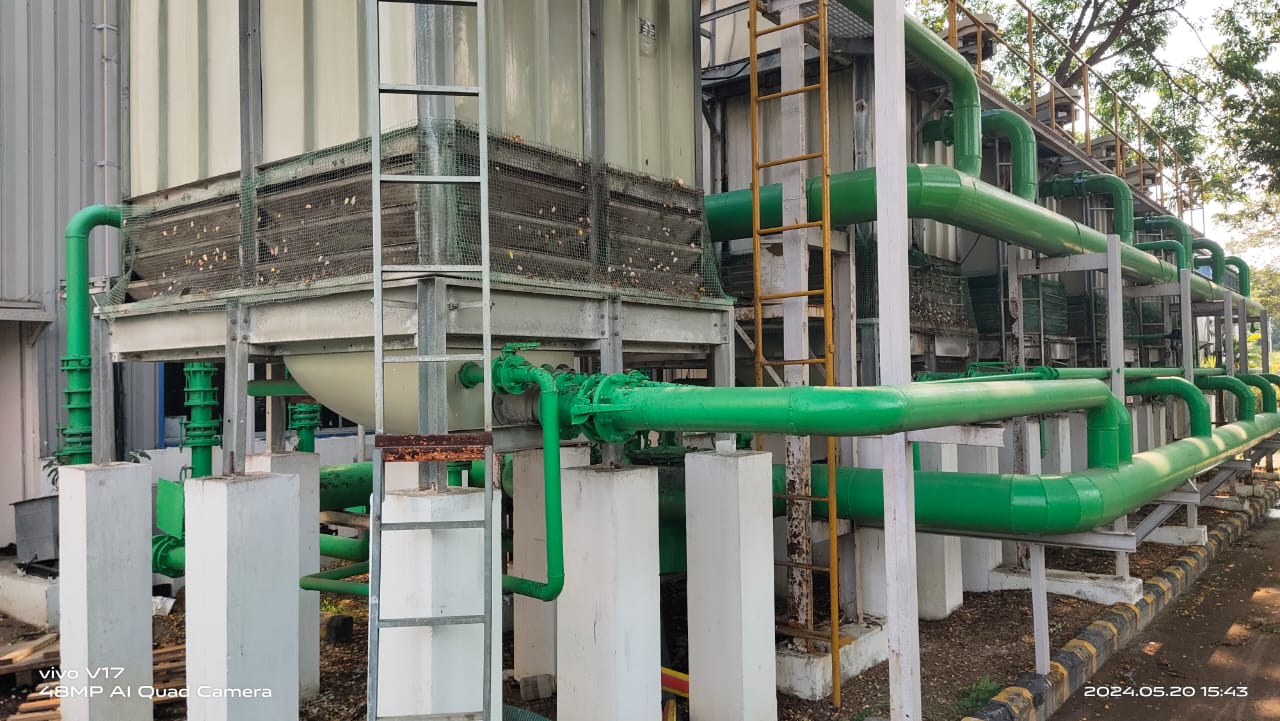
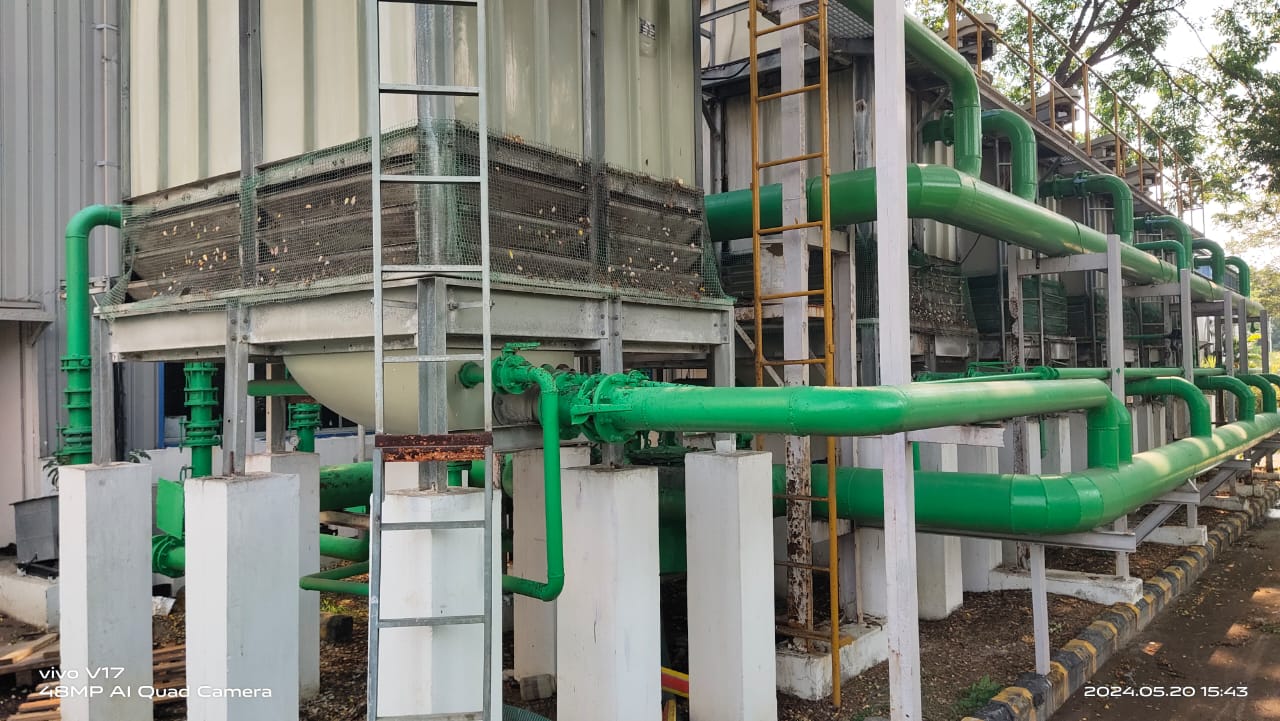
Cooling Tower: How to Enhance Energy Efficiency in Buildings
What is Cooling Tower in HVAC Systems A cooling tower is a specialized heat rejection device that extracts waste heat to the atmosphere through the cooling of a water stream…
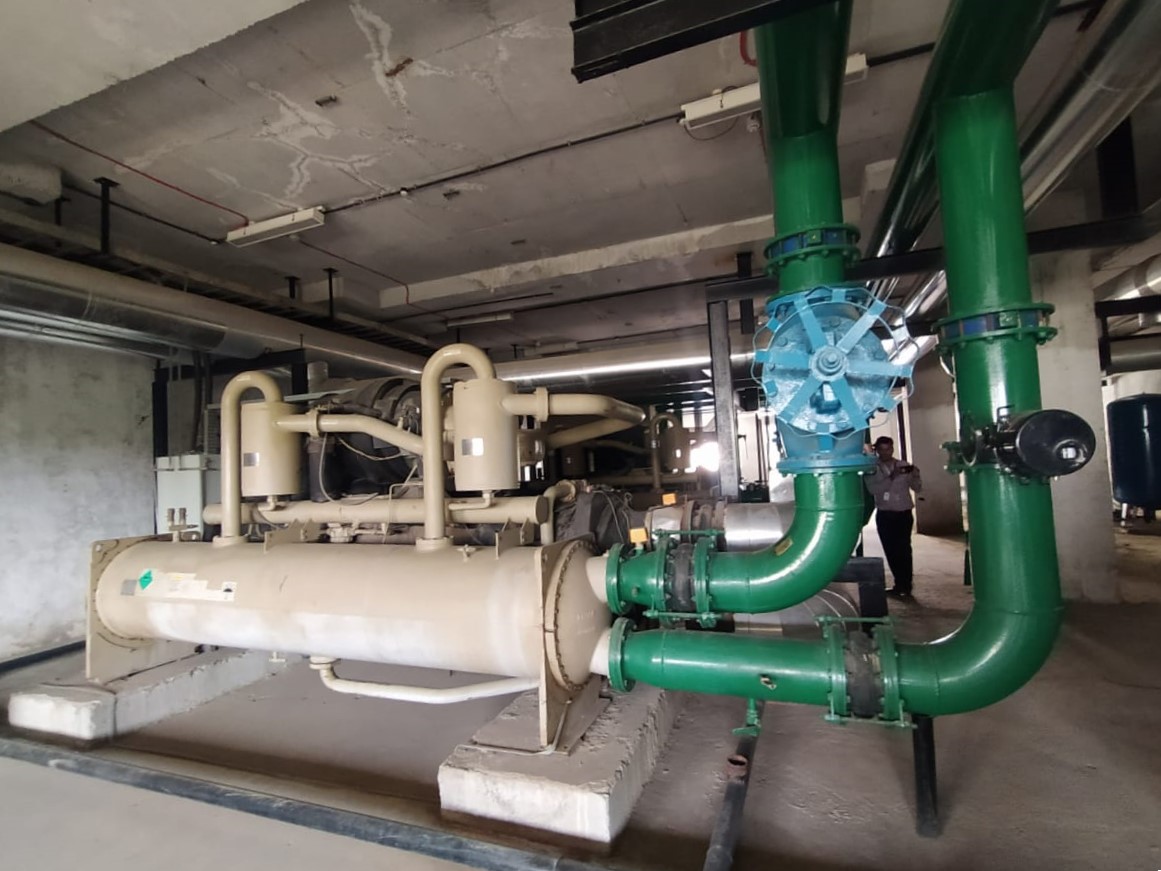
HVAC Chiller: The Ultimate Guide on Applications, and Benefits
An HVAC chiller is a vital component in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems designed to provide cooling by removing heat from a fluid via a refrigeration cycle. It…
Chilled Water Pipe: How to Enhance HVAC Systems
In the modern world of construction and industrial processes, the proper functioning of heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC) systems is critical to maintaining comfort, productivity and environmental sustainability. The…
Vibration Isolation: How to Optimize HVAC Performance
This article on vibration isolation covers the supply, delivery, installation, and testing of noise and vibration control equipment used to isolate various mechanical devices in HVAC systems. The purpose of…